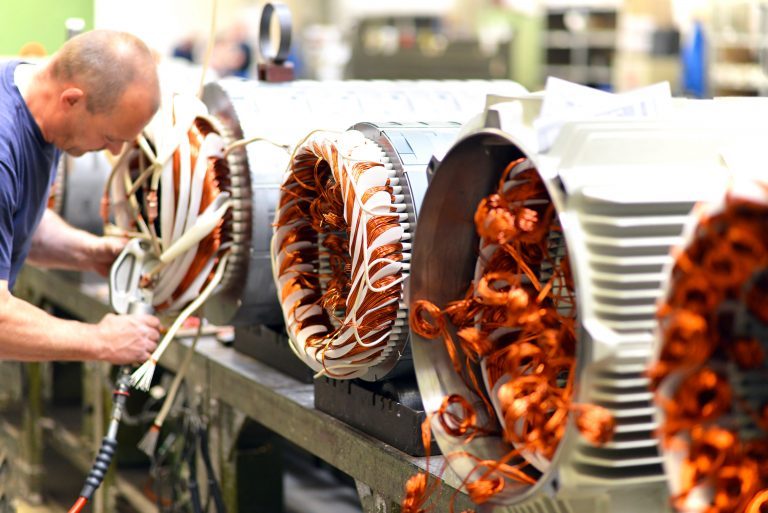
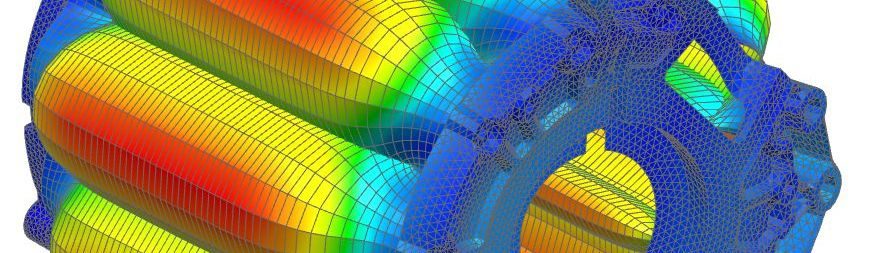
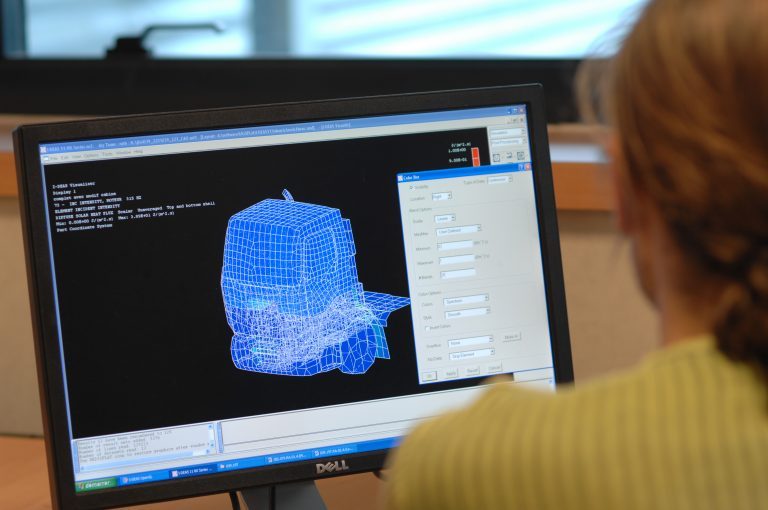
Electromagnetic simulation is an essential design tool for electrical machines, enabling mechanical, thermal and energy performance to be assessed and optimized. However, it is important to note that the acoustic behavior of electrical machines is often neglected in their design, even though the noise emitted by electric motors can be very annoying.
In all industrial sectors, electrical machines emit electromagnetic noise, vibrations and shock waves. In the railway sector, for example, traction motors are a source of exterior and interior noise. In the automotive sector, traction motors can reduce exterior noise, but interior noise can become a nuisance, particularly with the increasing power density of electric motors.
It is therefore important to take acoustic, vibratory and thermal aspects into account when designing electric machines to reduce noise and vibration to acceptable levels. Recent advances in electromagnetic simulation have enabled us to gain a better understanding of the acoustic behavior of electrical machines, and to develop strategies for reducing noise and vibration.
Vibratec has developed an innovative method for optimizing the electromagnetic design of electric motors with a view to reducing noise pollution. This method is based on determining the space-frequency content of the excitation applied to the stator, and can be applied to a wide variety of electric motors, including traction motors used in electric, hybrid and rechargeable vehicles.
Ultimately, electromagnetic simulation is a key tool for designing quiet, high-performance electric machines. By integrating acoustic, vibratory and thermal aspects early in the design process, engineers can develop electric machines that meet NVH (Noise, Vibration and Harshness) specifications and offer a more pleasant user experience, while ensuring the safety and durability of machine components.